Source code for any runtime environment of VCF Automation can also be used independently from the appliance. This allows us to create scripts that runs inside of and outside from VCF Automation. So it could be necessary to detect whether the source code is executed in VCF Automation or not.
Detect if Script is Executing in VCF Automation
JavaScript
The Rhino engine is used in the JavaScript runtime environment of VCF Automation. It works directly on the orchestration appliance. That is why the environment variables of VCF Automation can be read and this is very interesting. When the command printenv is entered in a terminal window, many fewer environment variables are displayed than when the same command is executed in an action. The best way is to get the environment variables it to use an approach, which is presented in this post:
Execute Operating System Commands.
var command =
System.getModule("de.stschnell").executeCommand(["printenv"]);
var commandOutput = command.output;
System.log(commandOutput);
|
When the code above is executed, many environment variables were displayed that were specific to VCF Automation. Here a selection:
/**
* ABX_SERVICE_PORT
* ABX_SERVICE_SERVICE_HOST
* ORCHESTRATION_UI_PORT
* ORCHESTRATION_UI_SERVICE_HOST
* TENANT_MANAGEMENT_UI_PORT
* TENANT_MANAGEMENT_UI_SERCICE_HOST
* VCO_CONTROLCENTER_SERVICE_PORT
* VCO_CONTROLCENTER_SERVICE_SERVICE_HOST
* VCO_SERVICE_PORT
* VCO_SERVICE_SERVICE_HOST
*/
|
So I tested the following tiny snippet:
var VcoControlcenterServicePort =
java.lang.System.getenv("VCO_CONTROLCENTER_SERVICE_PORT");
if (VcoControlcenterServicePort === null) {
System.log("VcoControlcenterServicePort not set");
} else {
System.log(VcoControlcenterServicePort);
}
|
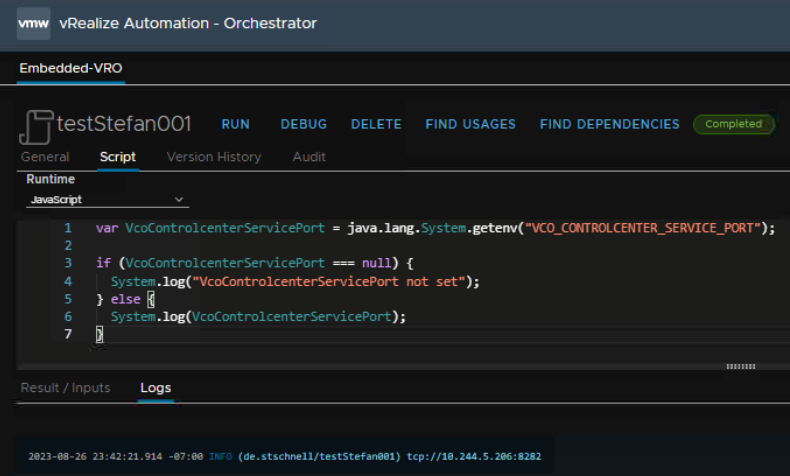
It delivers in the context of VCF Automation a result, and in the context of an emulation null.
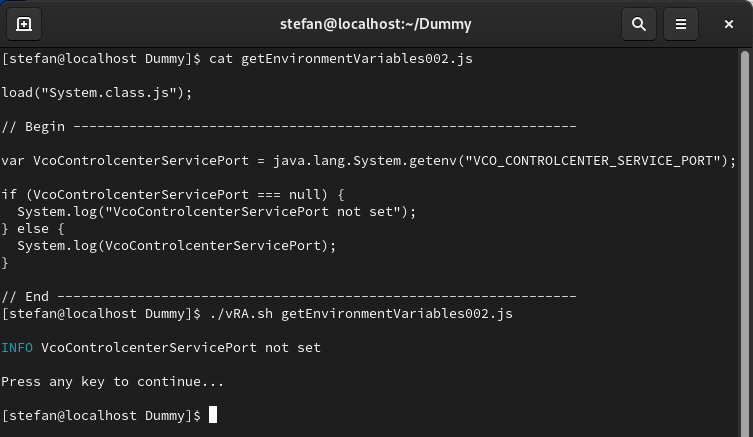
This seems to be a valid approach to differentiate whether a program is executed in the context of the JavaScript runtime environment of VCF Automation or not.
Python
The Python runtime environment of VCF Automation is executed in a container. To detect whether the script is executed in VCF Automation it is first checked whether the code runs in a Linux environment. If this is the case, it is checked whether it is a VMware Photon OS. If this is also the case, it is checked whether the host name begins with vco-app-, this identifies the orchestration appliance.
import json
import os
import platform
import subprocess
def isVCFAutomation() -> bool:
VCFAutomationFlag: bool = False
try:
if (platform.system().lower() == "linux"):
stdout: bytes = b""
stderr: bytes = b""
command: list = ["cat", "/etc/photon-release"]
cmd = subprocess.Popen(
command,
stdout = subprocess.PIPE,
stderr = subprocess.PIPE
)
stdout, stderr = cmd.communicate()
if "vmware photon os" in stdout.decode("utf-8").lower():
hostName: str = os.environ["HOSTNAME"]
httpProxy: str = os.environ["HTTP_PROXY"]
# Prelude is the name of the primary Kubernetes
# namespace in which all VCF application core
# services are executed. The name Prelude was
# the internal project code name during the
# development of the new vRA architecture and was
# retained as the name for the namespace in the
# finished product.
if (
hostName and hostName.startswith("vco-app-") and
httpProxy and "prelude" in httpProxy
):
VCFAutomationFlag = True
except:
pass
return VCFAutomationFlag
def handler(context: dict, inputs: dict) -> dict:
outputs: dict = {}
isVcfAutomation: bool = isVCFAutomation()
outputs = {
"status": "done",
"isVCFAutomation": isVcfAutomation
}
return outputs
|

