In heterogeneous IT corporate landscapes, there is a wide variety of different hardware and software. When deploying virtual machines (VM), the requester does not necessarily need to know all the details. On which architecture is the VM running? Which version of Python is available in the VM? Such questions and similar ones sometimes arise and need to be answered. This post shows how specific information can be detected at runtime.
Get System Information
Two approaches are presented here: On the one hand a Python program and on the other hand an Ansible playbook. The Python program can be run in any Python environment. The Python runtime from VCF Automation was used as an example here. This also as addition to the approaches described in the reference, but there with other execution environments.
Detecting system information about existing hardware or software can be very important to correctly provide or address software components that are dependent on it.
Python
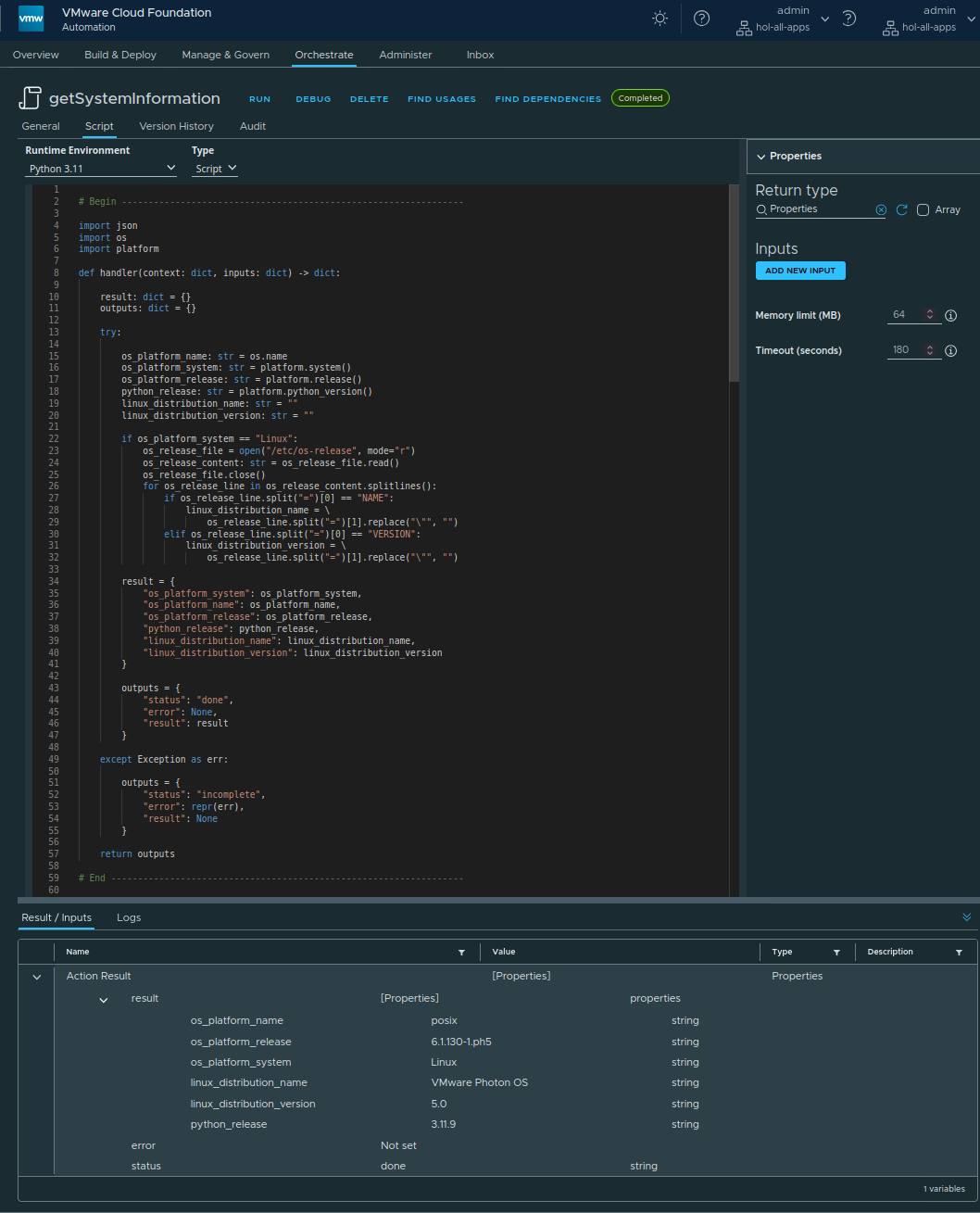
With the Python platform library and the os library some information are collected and made available in variables.
"""
@module de.stschnell
@version 0.1.0
@runtime python:3.11
@outputType Properties
"""
""" Collects some system information.
@author Stefan Schnell <mail@stefan-schnell.de>
@license MIT
@version 0.1.0
Checked with VCF Automation 9.0.0 from Orchestrator as action and from
CLI as Python program.
"""
import json
import os
import platform
def handler(context: dict, inputs: dict) -> dict:
result: dict = {}
outputs: dict = {}
try:
os_platform_name: str = os.name
os_platform_system: str = platform.system()
os_platform_release: str = platform.release()
os_platform_machine: str = platform.machine()
python_release: str = platform.python_version()
linux_distribution_name: str = ""
linux_distribution_version: str = ""
if os_platform_system == "Linux":
os_release_file = open("/etc/os-release", mode="r")
os_release_content: str = os_release_file.read()
os_release_file.close()
for os_release_line in os_release_content.splitlines():
if os_release_line.split("=")[0] == "NAME":
linux_distribution_name = \
os_release_line.split("=")[1].replace("\"", "")
elif os_release_line.split("=")[0] == "VERSION":
linux_distribution_version = \
os_release_line.split("=")[1].replace("\"", "")
result = {
"os_platform_system": os_platform_system,
"os_platform_name": os_platform_name,
"os_platform_release": os_platform_release,
"os_platform_machine": os_platform_machine,
"python_release": python_release,
"linux_distribution_name": linux_distribution_name,
"linux_distribution_version": linux_distribution_version
}
outputs = {
"status": "done",
"error": None,
"result": result
}
except Exception as err:
outputs = {
"status": "incomplete",
"error": repr(err),
"result": None
}
return outputs
|
Ansible
In Ansible the gathered facts are used for the detection. The result is very similar to the Python approach. In addition further interesting information is also detected.
---
# Collect some system information of the managed node.
#
# @author Stefan Schnell <mail@stefan-schnell.de>
- name: Get system details of the managed host
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: true
tasks:
- name: Print Ansible version
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "ansible_version: {{ ansible_version.full }}"
- name: Get OS platform system
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
os_platform_system: "{{ ansible_facts.system }}"
- name: Print OS platform system
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "os_platform_system: {{ os_platform_system }}"
- name: Print OS platfrom release
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "os_platform_release: {{ ansible_facts.kernel }}"
- name: Print OS platform machine
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "os_platform_machine: {{ ansible_facts.architecture }}"
- name: Print Python release
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "python_release: {{ ansible_facts.python_version }}"
- name: Get Linux OS information
when: os_platform_system == "Linux"
block:
- name: Get Linux OS information
changed_when: os_details.rc != 0
register: os_details
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: cat /etc/os-release
- name: Set Linux OS name variable
loop: "{{ os_details.stdout_lines }}"
when: item.split('=').0 == "NAME"
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
os_name: "{{ item.split('=').1 }}"
- name: Print Linux OS name
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "linux_distribution_name: {{ os_name }}"
- name: Set Linux OS version variable
loop: "{{ os_details.stdout_lines }}"
when: item.split('=').0 == "VERSION"
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
os_version: "{{ item.split('=').1 }}"
- name: Print Linux OS version
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "linux_distribution_version: {{ os_version }}"
- name: Get Bash version
changed_when: bash_version.rc != 0
register: bash_version
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: bash --version
- name: Print Bash version
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ bash_version.stdout_lines.0 }}"
- name: Call command whoami
changed_when: whoami.rc != 0
register: whoami
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: whoami
- name: Print whoami
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ whoami.stdout_lines }}"
- name: Get environment variables
changed_when: environment_variables.rc != 0
register: environment_variables
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: printenv
- name: Print environment variables
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ environment_variables.stdout_lines }}"
- name: Get Linux OS commands
when: os_platform_system == "Linux"
block:
- name: Get commands from /usr/bin
changed_when: commands.rc != 0
register: commands
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: ls /usr/bin
- name: Print commands from /usr/bin
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ commands.stdout_lines }}"
|
Conclusion
The detection of information during runtime offers several possibilities for responding flexibly to different hardware and software installations. Or only simply to know exactly what to be found.
References
