Basic explanations of unit tests can be found in the post
Unit Test Library for Actions.
Using Unit Test Modules in Python Runtime Environment
Python offers in its standard library the doctest and unittest modules for unit testing. To run this kind of tests it is therefore not necessary to install third-party packages, which is very important for air-gapped environments. This post shows how these modules can be used in VCF Automation.
doctest
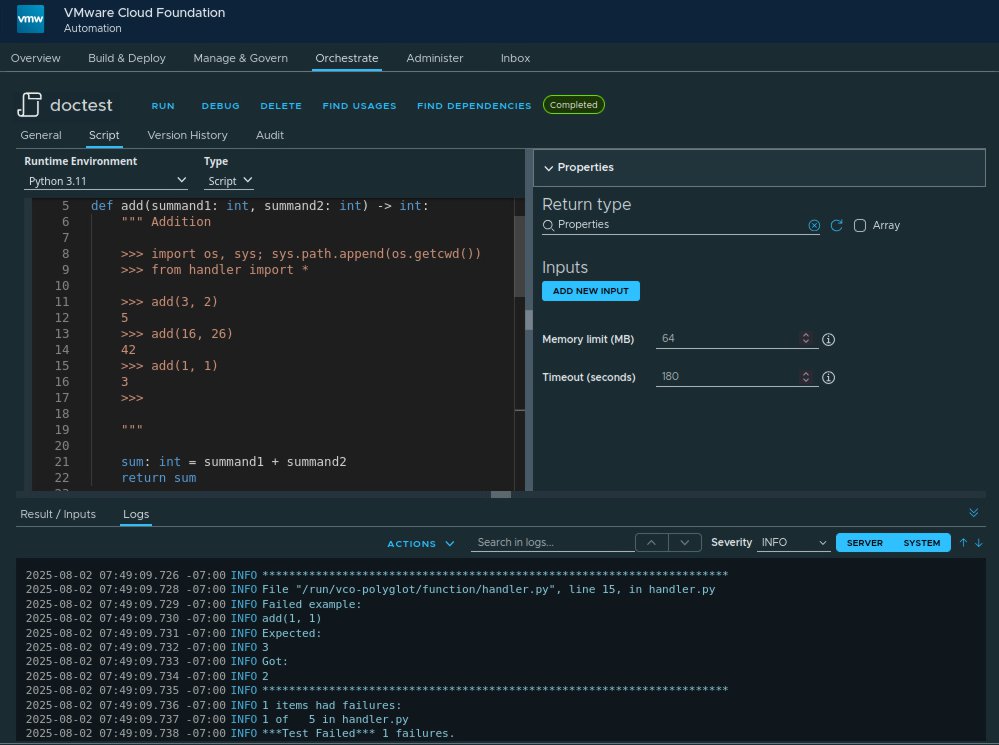
The
Python doctest module is a standard library that makes it possible to use docstrings as unit tests, bases on the output from the standard Python interpreter shell. With doctest unit tests can be written directly in the code with minimal overhead.
doctest uses a primary prompt >>> which is followed by the tested commands. It is possible to use a secondary prompt ... when continuing commands on multiple lines. The expected result of the executing command is on the following line. A line starting with the primary prompt marks the end.
doctests are good for simple tests and simplifies the documentation, because test cases and examples are directly included in the code.
"""
@author Stefan Schnell <mail@stefan-schnell.de>
@license MIT
@version 1.0
@runtime python:3.11
@outputType Properties
Checked with Aria Automation 8.18.1 and VCF Automation 9.0.0
"""
import doctest
import json
import os
def add(summand1: int, summand2: int) -> int:
""" Addition
>>> import os, sys; sys.path.append(os.getcwd())
>>> from handler import *
>>> add(3, 2)
5
>>> add(16, 26)
42
>>> add(1, 1)
3
>>>
"""
sum: int = summand1 + summand2
return sum
def handler(context: dict, inputs: dict) -> dict:
""" Aria Automation standard handler.
"""
result: dict = {}
outputs: dict = {}
try:
doctest.testfile(os.path.basename(__file__))
outputs = {
"status": "done",
"error": None,
"result": result
}
except Exception as err:
outputs = {
"status": "incomplete",
"error": repr(err),
"result": None
}
return outputs
|
Hint: It is necessary to add the import statement and the sys.path.append method in the docstring. The Python shell, which runs the doctest, needs this information to find and load the script. As far as known is the name of the generated Python script always handler.py.
unittest
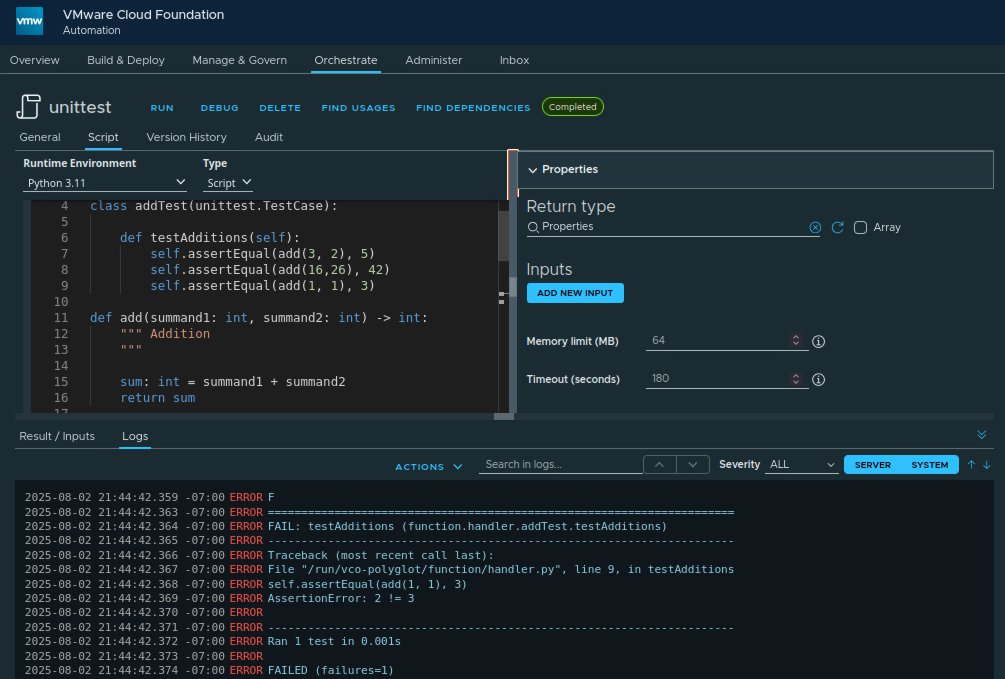
The
Python unittest module is a standard library which contains a unit testing framework. It supports test automation and many features to write unit tests. It includes assertion methods that check specific conditions in tests and setup and teardown methods to manage the test environment.
unittests are good for not so simple tests. The difference to doctest is that the test cases are defined outside of the program code, program documentation and test description are separated, but this is of secondary importance for the use in VCF Automation. The clarity of the tests through the assert method names helps to quickly understand the purpose and expected behavior of a test.
"""
@author Stefan Schnell <mail@stefan-schnell.de>
@license MIT
@version 1.0
@runtime python:3.11
@outputType Properties
Checked with Aria Automation 8.18.1 and VCF Automation 9.0.0
"""
import json
import unittest
class addTest(unittest.TestCase):
def testAdditions(self):
self.assertEqual(add(3, 2), 5)
self.assertEqual(add(16,26), 42)
self.assertEqual(add(1, 1), 3)
def add(summand1: int, summand2: int) -> int:
""" Addition
"""
sum: int = summand1 + summand2
return sum
def handler(context: dict, inputs: dict) -> dict:
""" Aria Automation standard handler.
"""
result: dict = {}
outputs: dict = {}
try:
tests: list = [
addTest("testAdditions")
]
suite = unittest.TestSuite(tests = tests)
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner(verbosity = 2)
runner.run(suite)
outputs = {
"status": "done",
"error": None,
"result": result
}
except Exception as err:
outputs = {
"status": "incomplete",
"error": repr(err),
"result": None
}
return outputs
|
Hint: The unit test is executed here in the form of a test suite. The use of unittest.main() is not possible because the __main__ method originates from the caller index.py, which is created by VCF Automation to call handler.py.
Conclusion
In principle both unit test modules of the Python standard library can be used in VCF Automation. However, the Python call stack of VCF Automation must be taken into account to enable its usage.
The actions built here are the unit tests. Of course, other actions can also be called in the tested functions. doctest is a good choice for simple tests, while unittest are more suitable for more complex applications.
Addendum
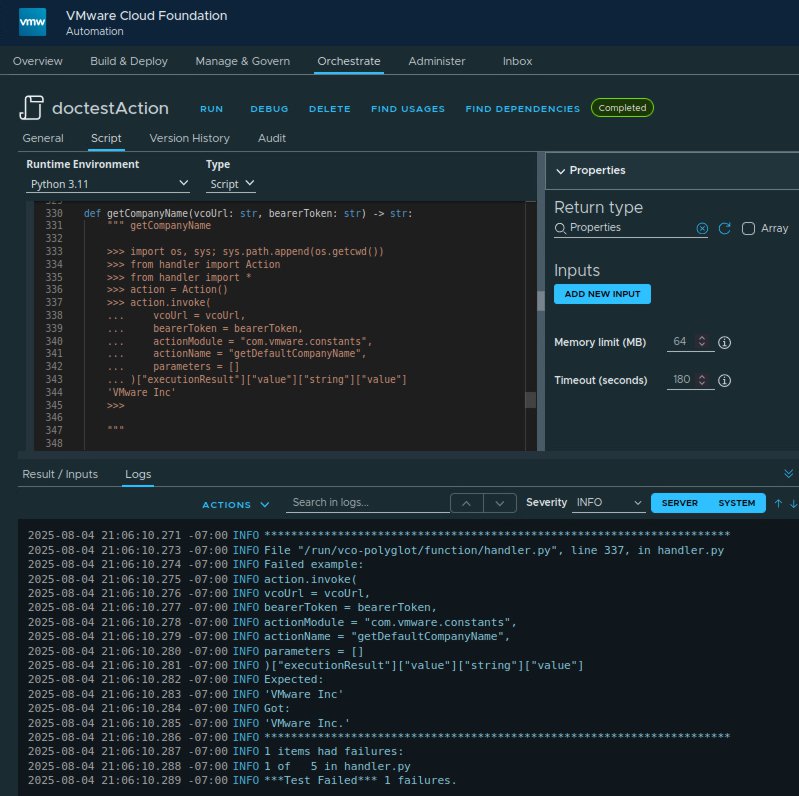
The following examples show how to use the doctest and unittest modules with an action call.
doctest
"""
@author Stefan Schnell <mail@stefan-schnell.de>
@license MIT
@version 1.0
@runtime python:3.11
@outputType Properties
Checked with Aria Automation 8.18.1 and VCF Automation 9.0.0
"""
from util.action import Action
import doctest
import json
import os
def getCompanyName(vcoUrl: str, bearerToken: str) -> str:
""" getCompanyName
>>> import os, sys; sys.path.append(os.getcwd())
>>> from util.action import Action
>>> from handler import *
>>> action = Action()
>>> action.invoke(
... vcoUrl = vcoUrl,
... bearerToken = bearerToken,
... actionModule = "com.vmware.constants",
... actionName = "getDefaultCompanyName",
... parameters = []
... )["executionResult"]["value"]["string"]["value"]
'VMware Inc.'
>>>
"""
action = Action()
companyName: str = action.invoke(
vcoUrl = vcoUrl,
bearerToken = bearerToken,
actionModule = "com.vmware.constants",
actionName = "getDefaultCompanyName",
parameters = []
)["executionResult"]["value"]["string"]["value"]
return companyName
def handler(context: dict, inputs: dict) -> dict:
""" Aria Automation standard handler.
"""
result: str = ""
outputs: dict = {}
try:
vcoUrl: str = context["vcoUrl"]
bearerToken: str = context["getToken"]()
doctest.testfile(
os.path.basename(__file__),
globs = {
"vcoUrl": vcoUrl,
"bearerToken": bearerToken
}
)
"""
result = getCompanyName(
vcoUrl = vcoUrl,
bearerToken = bearerToken
)
print(result)
"""
outputs = {
"status": "done",
"error": None,
"result": result
}
except Exception as err:
outputs = {
"status": "incomplete",
"error": repr(err),
"result": None
}
return outputs
|
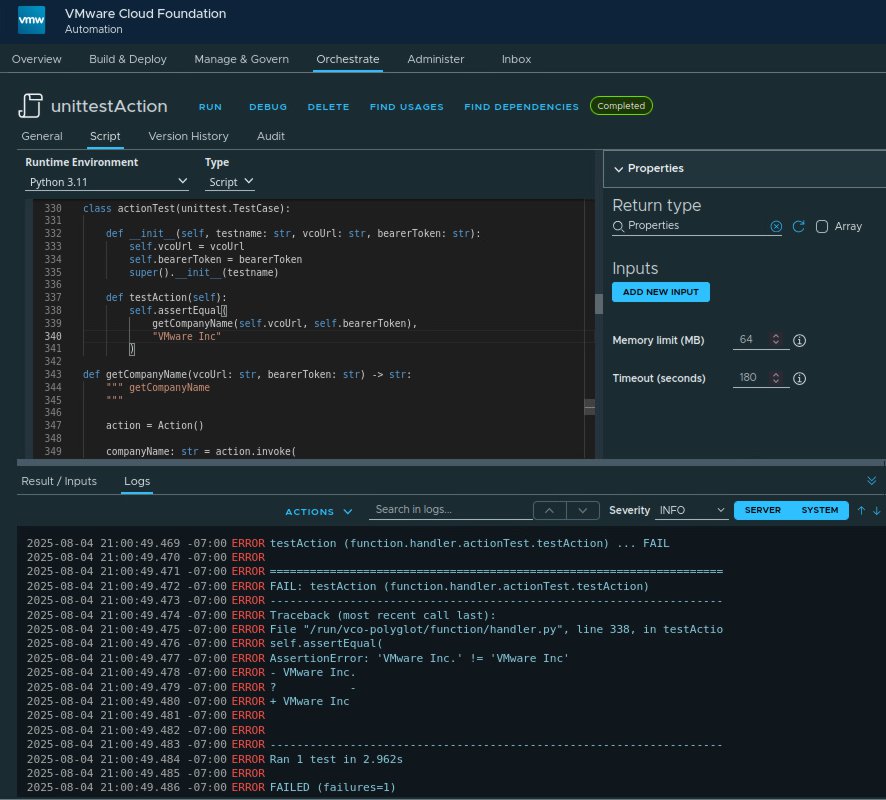
unittest
"""
@author Stefan Schnell <mail@stefan-schnell.de>
@license MIT
@version 1.0
@runtime python:3.11
@outputType Properties
Checked with Aria Automation 8.18.1 and VCF Automation 9.0.0
"""
from util.action import Action
import json
import unittest
class actionTest(unittest.TestCase):
def __init__(self, testname: str, vcoUrl: str, bearerToken: str):
self.vcoUrl = vcoUrl
self.bearerToken = bearerToken
super().__init__(testname)
def testAction(self):
self.assertEqual(
getCompanyName(self.vcoUrl, self.bearerToken),
"VMware Inc."
)
def getCompanyName(vcoUrl: str, bearerToken: str) -> str:
""" getCompanyName
"""
action = Action()
companyName: str = action.invoke(
vcoUrl = vcoUrl,
bearerToken = bearerToken,
actionModule = "com.vmware.constants",
actionName = "getDefaultCompanyName",
parameters = []
)["executionResult"]["value"]["string"]["value"]
return companyName
def handler(context: dict, inputs: dict) -> dict:
""" Aria Automation standard handler.
"""
result: dict = {}
outputs: dict = {}
try:
vcoUrl: str = context["vcoUrl"]
bearerToken: str = context["getToken"]()
suite = unittest.TestSuite()
suite.addTest(
actionTest("testAction", vcoUrl, bearerToken)
)
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner(verbosity = 2)
runner.run(suite)
"""
result = getCompanyName(
vcoUrl = vcoUrl,
bearerToken = bearerToken
)
print(result)
"""
outputs = {
"status": "done",
"error": None,
"result": result
}
except Exception as err:
outputs = {
"status": "incomplete",
"error": repr(err),
"result": None
}
return outputs
|
References



